3.6 Physical Cosmology
Newton’s mechanics is good enough to be applied to the solar system, but as a cosmological theory it is completely false insofar as it still considered, like Aristotle, the stars to be fixed and the Universe outside the solar system to be static, as we explained in chapter II. Although a dynamic Universe could have been easily predicted according to Newton’s theory of gravity, the belief in the Aristotelian static Universe was so deep and strong that it persisted for more than three centuries after Newton, even after Einstein formulated his theory of General Relativity. As Hawking said:
“Even Einstein, when he formulated the general theory of relativity in 1915, was so sure that the Universe had to be static that he modified his theory to make this possible, introducing a so-called cosmological constant into his equations.” Hawking (1998)
This of course was soon proved to be wrong, and everybody now knows that the cosmos, outside the solar system, is in continuous motion. Einstein himself later considered the cosmological constant to be his greatest plunder, although it had actually returned later in a different manner as we shall see in section 9.21. We will see also in chapter IV that Ibn al-Arabi declared quite plainly in different occasions that the stars can’t be fixed at all, and he even gave numbers and units to the speed of their proper motion, which are consistent with the latest accurate measurements.
In 1718, Edmund Halley (1656-1742) compared the positions of stars, as they were recorded by the Babylonians and other ancient astronomers, with the latest observations, and he realized that the positions of some of the stars were not the same as they had been thousands of years earlier. Some of the stars were in fact slightly displaced from the rest by a small but noticeable amount. This is called “proper motion”, which is the apparent motion of the star, perpendicular to the line of sight, in relation to the background stars that are very far away. Actually, Ibn al-Arabi noticed this change five centuries before that when he mentioned in the Meccan Revelations that “it was written in one of the Pyramids of Egypt, that it had been built when (the constellation of) Aquila was in Leo, and now it is clearly in Capricorn as we see it today (around 1234 AD). This means that the ‘fixed stars’ are actually moving in the zodiac!” [I.141.18].
In 1783, William Herschel discovered the solar motion, the Sun’s motion relative to the stars in its galactic neighborhood, and he also showed that the Sun and other stars are arranged like the “grains of abrasive in a grindstone”, which is now called the Milky Way galaxy. More than a century later, in 1924, Hubble was able to measure distances to some stars, based on the redshift, and he showed that some bright dots that we see in the sky are actually other galaxies like our own, although they look so small because they are very far away.
The Aristotelian theory of a static Universe had to be reviewed after Hubble’s discovery of the redshift of light coming from all distant stars, which indicated that everything in the Universe is actually moving.
When these discoveries were combined with the theoretical calculations based on Schwarzschild’s solutions of Einstein’s Field Equations, the Big Bang model was developed and became the most prevailing theory in cosmology, as we shall discuss it further in section 6.3, but before that, the Steady-State theory, that will be reviewed in section 6.1, tried to explain the expansion of the Universe by supposing a continuous creation of matter that filled the space produced by the expansion. However, the discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation in 1965 caused the Steady-State model to be completely discarded, because the background radiation was interpreted as the faint afterglow of the intense radiation of the Big Bang event. Other important models or variations, such as the Oscillating Universe, will be also discussed in section 6.2 before we concentrate on the Big Bang and how it developed into the current Standard Model of cosmology, the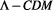 model, that will be reviewed in section 6.6.
model, that will be reviewed in section 6.6.
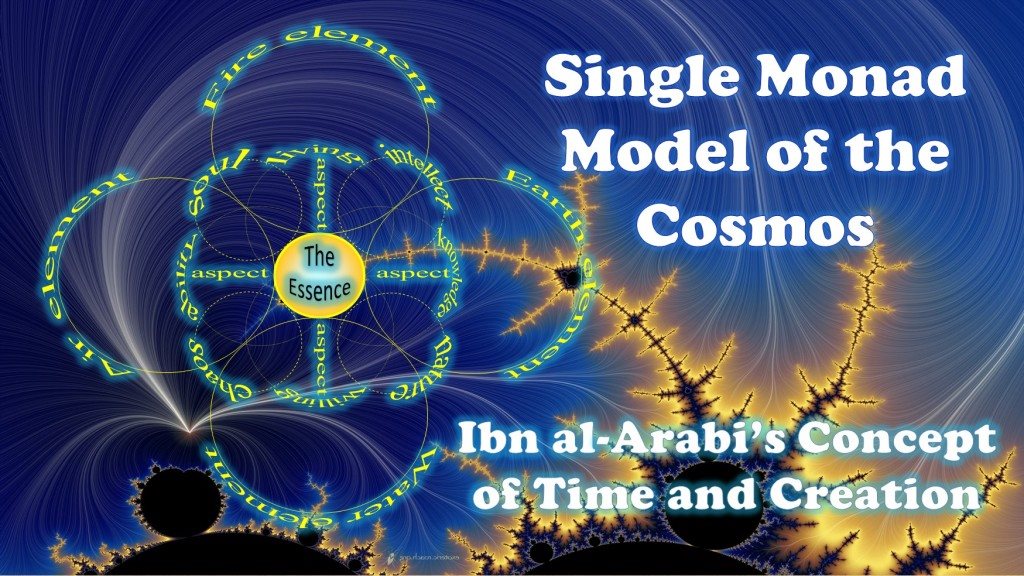
However, we will see in the following chapters, that the Single Monad Model of the cosmos, and the resulting genuinely-complex time-time Euclidean geometry of the Duality of Time hypothesis, will introduce essential modifications on the origin, size and structure of the cosmos. This may combine together the Steady-State theory, the Oscillating Universe, and the Big Bang model, with their main different variations, all in one unified view that makes all the major physics theories and cosmological models complementary, despite their apparent discrepancies.
This eccentric proposition will be illustrated further in chapters IV and VI, but we can roughly say that since vacuum is the flat space, or the aether which is the ground state for matter particles that are its excited states which are being re-created in the inner time, the physical Universe that we observe have started at some instance in the past that we call the Big Bang, but not as a singularity of hot and dense space, because absolute vacuum is no longer empty, but it is an infinite flat space that is being re-created in the inner levels of time; so the beginning of this Universe is not when the inner time started, but when the outer time started, which simply corresponds to exciting the instances of aether into particles that then start to develop and condense into matter and then, eventually, make stars and galaxies. So the Big Bang is only a ripple in the infinite flat space, and it is actually one of many disconnected ripples, each making its own Universe. On the large scale, therefore, the whole Universe, or multiverse, is described by the perfect cosmological principle, which is the basis for the Steady-state theory, because these ripples may randomly start and end, or oscillate, without violating the law of entropy, since they are part of a larger system, and this expansion and contraction is described by scenarios similar to the (eternal) inflation. So as we can see from this extremely simplified view, all the major theories are different views of the reality, each is correct from certain aspects, while the Duality of Time makes them complementary.
What is even more eccentric is that, since space-time is now dynamic and self-contained, our own Universe is actually much smaller than we are observing, but we are simply looking at repeated different relics of its long history, because light keeps coming back again, showing us various images distorted by gravitational lensing. We will come back to these ideas in more details in the coming chapters once we finish this essential review.