DUALITY OF TIME:
Complex-Time Geometry and Perpetual Creation of Space
Search Inside this Book
2.17.1 Entropy
Clausius also realized that heat engines could utilize only some of the available heat to do work, and from this he developed the concept of entropy, which he showed that it always increased in any spontaneous natural process. This in turn established the second law of thermodynamics, which states that, in isolated systems, the total entropy can only increase over time.
Entropy is related to the number of microscopic configurations that a thermodynamic system can have when in a state as specified by some macroscopic variables. Assuming for simplicity that each of the microscopic configurations is equally probable, the entropy of the system is the natural logarithm of that number of configurations
is the natural logarithm of that number of configurations , multiplied by Boltzmann constant
, multiplied by Boltzmann constant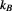 which has the dimension of energy divided by temperature:
which has the dimension of energy divided by temperature:
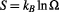
(2.4)
In the modern microscopic interpretation of entropy in statistical mechanics, entropy is the amount of additional information needed to specify the exact physical state of a system, given its thermodynamic specification.
The second law of thermodynamics is one of the fundamental laws of nature. After developing General Relativity, in the 1920s, many theoretical physicists, including Einstein, considered the possibility of cyclic models in which the universe follows indefinite self-sustaining cycles of eternal series of expansion and contraction. We shall briefly discuss these models in chapter III.
Another important puzzle associated with the second law of thermodynamics is the entropic arrow of time, because it requires a particular direction for time, unlike most other laws of physics which are time-symmetric. The Arrow of Time concept was developed by Arthur Eddington (1882-1944 AD) in 1927 and it is still an unsolved general physics problem. as we indicated in chapter I and will discuss further in chapter V, the Duality of Time is intrinsically built on one time direction, both for the inner and outer levels, and the arrow of time will be explicitly expressed in the equations that will also show how two opposite arrows of time combine to make one (two-directions) dimension of space. We will also discuss the entropic and other similar arrows of time that result from various other natural phenomena when we review modern physics and cosmology in chapter III.
... Space Transcendence Read this short concise exploration of the Duality of Time Postulate: DoT: The Duality of Time Postulate and Its Consequences on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics ...
... principle shows mathematically that the product of the standard deviation, or the uncertainty, in the position and momentum of a particle could never be less than halve of the value of the reduced Planck’s constant ( ): (3.18) For this reason, the position and momentum are known as ...
... in position, entanglement and coherence. The uncertainty principle is inherent in the properties of all wave-like systems, so it arises in Quantum Mechanics simply due to the wave nature of MATTER PARTICLE s and quantum objects, as we explained in section 4.4.1. Therefore, it should not be ...
... y serious consideration for large bodies, but becomes very important for microscopic systems. In 1932, Heisenberg won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work that has considerable impact on QUANTUM PHYSICS . The uncertainty principle shows mathematically that the product of the standard dev ...
... example, the momentum of the system. This, however, does not have any serious consideration for large bodies, but becomes very important for microscopic systems. In 1932, Heisenberg won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work that has considerable impact on quantum physics. The uncertainty ...
... e exploration of the Duality of Time Postulate: DoT: The Duality of Time Postulate and Its Consequences on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics ...
... in position, entanglement and coherence. The uncertainty principle is inherent in the properties of all wave-like systems, so it arises in Quantum Mechanics simply due to the wave nature of MATTER PARTICLES and quantum objects, as we explained in section 4.4.1. Therefore, it should not be ...
... lity of oneness. In wave mechanics, the uncertainty relation between position and momentum arises because the expressions of the wave-function, in the two corresponding orthonormal bases in Hilbert space, are Fourier transforms of one another, because position and momentum are conjugate va ...
... in position, entanglement and coherence. The uncertainty principle is inherent in the properties of all wave-like systems, so it arises in Quantum Mechanics simply due to the wave nature of MATTER PART icles and quantum objects, as we explained in section 4.4.1. Therefore, it should not be ...
... hat measurements of certain systems cannot be made without affecting the system. We shall also discuss the observer effect in section 4.4.5 and in chapter VI because it is one of the subtle QUANTUM PROPERTIES that cannot be explained without taking into account the reality of oneness. In w ...
... ld never be less than halve of the value of the reduced Planck’s constant ( ): (3.18) For this reason, the position and momentum are known as complementary variables. Henceforth, the COMPLEMENTARITY PRINCIPLE was formulated later by Bohr; that quantum objects have certain complement ...
... ange at a certain position, entanglement and coherence. The uncertainty principle is inherent in the properties of all wave-like systems, so it arises in Quantum Mechanics simply due to the WAVE NATURE of matter particles and quantum objects, as we explained in section 4.4.1. Therefore, it ...