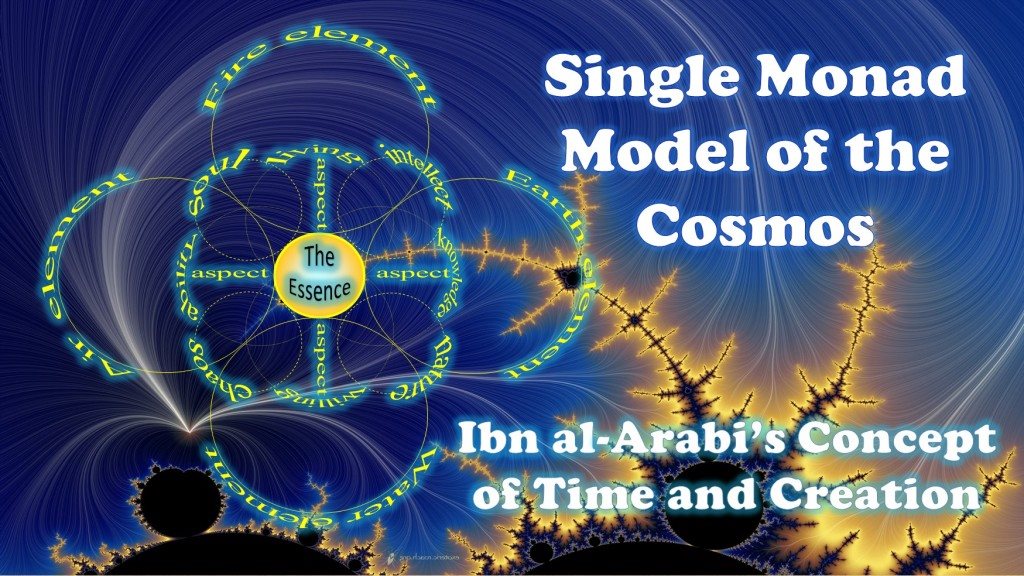
THE SINGLE MONAD MODEL OF THE COSMOS:
Ibn al-Arabi's Concept of Time and Creation
Search Inside this Book
9. Time in Modern Science:
Quantum Field Theory and General Relativity are the most well-established modern fundamental theories of physics. According to these theories, spacetime is a collection of points called 'spacetime locations' where physical events occur. Spacetime is a four-dimensional continuum, with physical time being a distinguished, one-dimensional sub-space of this continuum, but no longer a separate entity nor space: space and time are always taken together as one entity.
In 1908, the mathematician Hermann Minkowski, Einstein's teacher, was the first person to realize that spacetime is more fundamental than time or than space alone. As he put it:
The views of space and time which I wish to lay before you have sprung from the soil of experimental physics, and therein lies their strength. They are radical. Henceforth space by itself and time by itself are doomed to fade away into mere shadows, and only a kind of union of the two will preserve an independent reality.
(Pais 1982: 152)
The metaphysical assumption behind Minkowski's remark is that what is independently real is what does not vary from one reference frame to another. It follows that the division of events into the past ones, the present ones, and the future ones is also not independently real.
In contrary to the classical Newtonian view, time intervals depend greatly on the observer's frame of reference. In classical mechanics, and based on common sense, if the time interval between two lightning flashes is 100 seconds on someone's clock, then the interval also is 100 seconds on your clock, even if you are flying by at an incredible speed. Einstein rejected this piece of common sense in his 1905 special theory of relativity when he declared that the time interval (and the distance) between two events depends on the observer's reference frame. He says that every reference-body has its own particular time; unless we are told the reference-body to which the statement of time refers, there is no meaning in a statement of the time of an event (Einstein 1920: ch. 9). Thus each reference frame (or reference-body) divides spacetime differently into its time part and its space part.
... Space Transcendence Read this short concise exploration of the Duality of Time Postulate: DoT: The Duality of Time Postulate and Its Consequences on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics ...
... It follows that the division of events into the past ones, the present ones, and the future ones is also not independently real. In contrary to the classical Newtonian view, time intervals DEPEND GREATLY on the observer's frame of reference. In classical mechanics, and based on common sen ...
... between two events depends on the observer's reference frame. He says that every reference-body has its own particular time; unless we are told the reference-body to which the statement of TIME REFER s, there is no meaning in a statement of the time of an event (Einstein 1920: ch. 9). Thus ...
... nce-body to which the statement of time refers, there is no meaning in a statement of the time of an event (Einstein 1920: ch. 9). Thus each reference frame (or reference-body) divides space TIME DIFFER ently into its time part and its space part. Read Other Books: The Single M ...
... 0 seconds on someone's clock, then the interval also is 100 seconds on your clock, even if you are flying by at an incredible speed. Einstein rejected this piece of common sense in his 1905 SPECIAL THEORY of relativity when he declared that the time interval (and the distance) between two ...
... rabi's Concept of Time and Creation by Mohamed Haj Yousef Search Inside this Book 9. Time in Modern Science: Quantum Field Theory and General Relativity are the most well-established modern FUNDAMENTAL THEORIES of physics. According to these theories, spacetime is a collection of points ca ...
... nce-body to which the statement of time refers, there is no meaning in a statement of the time of an event (Einstein 1920: ch. 9). Thus each reference frame (or reference-body) divides space TIME DIFFERENTLY into its time part and its space part. Read Other Books: The Single M ...
... rs, there is no meaning in a statement of the time of an event (Einstein 1920: ch. 9). Thus each reference frame (or reference-body) divides spacetime differently into its time part and its SPACE PART . Read Other Books: The Single Monad Model of the Cosmos: Ibn Arabi's View o ...
... g a distinguished, one-dimensional sub-space of this continuum, but no longer a separate entity nor space: space and time are always taken together as one entity. In 1908, the mathematician Hermann Minkowski, Einstein's teacher, was the first person to realize that spacetime is more fundam ...
... ement of time refers, there is no meaning in a statement of the time of an event (Einstein 1920: ch. 9). Thus each reference frame (or reference-body) divides spacetime differently into its TIME PART and its space part. Read Other Books: The Single Monad Model of the Cosmos: ...
... ime locations' where physical events occur. Spacetime is a four-dimensional continuum, with physical time being a distinguished, one-dimensional sub-space of this continuum, but no longer a SEPARATE ENTITY nor space: space and time are always taken together as one entity. In 1908, the math ...
... vary from one reference frame to another. It follows that the division of events into the past ones, the present ones, and the future ones is also not independently real. In contrary to the classical Newtonian view, time intervals depend greatly on the observer's frame of reference. In cla ...