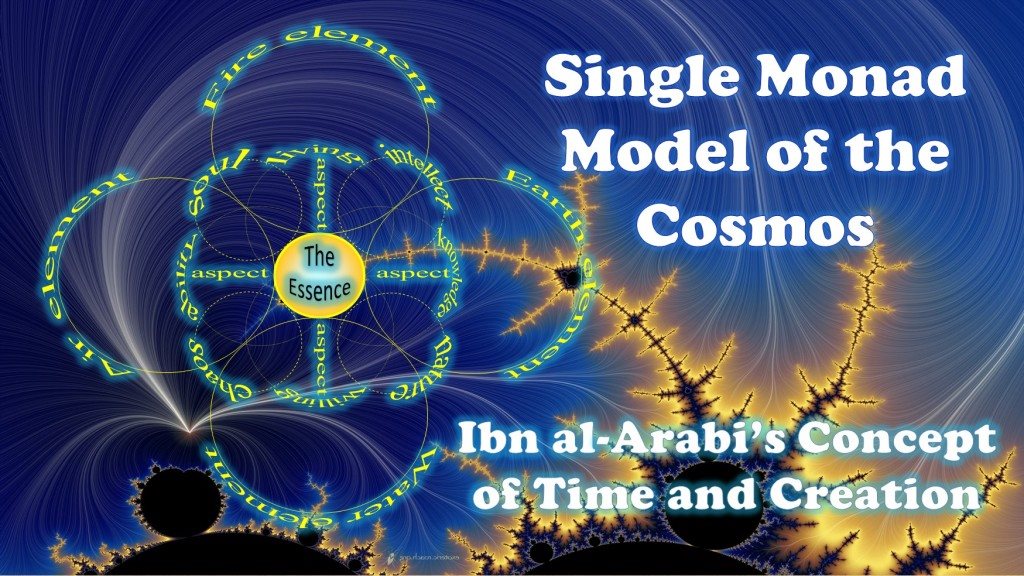
The Duality of Time Postulate and Its Consequences on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics
[
PDF Download]
Search Inside this Book
Method I (abrupt change of speed in the inner time):
The relativistic energy-momentum relation is derived in section 6.2.8 further below, but the simple mass-energy equivalence relation: 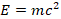 (without the “half”) can now be easily obtained from the same integration in equation 9 if, and only if, we suppose that the object, whose mass is
(without the “half”) can now be easily obtained from the same integration in equation 9 if, and only if, we suppose that the object, whose mass is 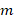 , moves from rest to
, moves from rest to  , or vice versa, in “zero time”, which of course will contradict the laws of physical motion because the acceleration would be infinite, and hence the force and the energy. Light does in fact behave in this manner, for example: in pair production, or when emitted or absorbed; but the photon is massless, unlike other particles and objects which have mass and suffer inertia and acceleration.
, or vice versa, in “zero time”, which of course will contradict the laws of physical motion because the acceleration would be infinite, and hence the force and the energy. Light does in fact behave in this manner, for example: in pair production, or when emitted or absorbed; but the photon is massless, unlike other particles and objects which have mass and suffer inertia and acceleration.
By introducing the duality of time and the resulting perpetual re-creation, this problem is solved because the conversion between mass and energy takes place, sequentially, in the inner levels of time, on all the massless geometrical points that constitute the particle, and this whole process appears as one instance in the outer level, as demonstrated in Figure 5 above.
So by integrating equation 9 directly from zero to 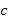 , which then becomes summation because it is an abrupt change, with only the two states of void and vacuum, corresponding to zero and
, which then becomes summation because it is an abrupt change, with only the two states of void and vacuum, corresponding to zero and 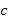 , respectively, and since the change in the outward time is zero, and here we also consider
, respectively, and since the change in the outward time is zero, and here we also consider 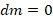 , since the apparent velocity does not change in this case, but we will also discuss relativistic mass in section 6.2.4 below; thus we obtain:
, since the apparent velocity does not change in this case, but we will also discuss relativistic mass in section 6.2.4 below; thus we obtain:
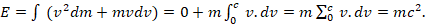 (11)
(11)
The difference between the above two cases that result in equations 9 and 11 is demonstrated in Figure 6.2.1, where in the first case the integration that gives the kinetic energy 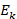 is the area of the triangle below the gradual arrow (1), while in the second case it is the area of the rectangle below the right angle arrow (2).
is the area of the triangle below the gradual arrow (1), while in the second case it is the area of the rectangle below the right angle arrow (2).
... Space Transcendence Read this short concise exploration of the Duality of Time Postulate: DoT: The Duality of Time Postulate and Its Consequences on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics ...
... sponding to zero and , respectively, and since the change in the outward time is zero, and here we also consider , since the apparent velocity does not change in this case, but we will also DISCUSS RELATIVISTIC mass in section 6.2.4 below; thus we obtain: � ...
... arch Inside this Book Method I (abrupt change of speed in the inner time): The relativistic energy-momentum relation is derived in section 6.2.8 further below, but the simple mass-energy EQUIVALENCE RELATION : (without the “half”) can now be easily obtained from the same integratio ...
... (11) The difference between the above two cases that result in equations 9 and 11 is demonstrated in Figure 6.2.1, where in the first case the integration that gives the KINETIC ENERGY is the area of the triangle below the gradual arrow (1), while in the second case i ...
... abrupt change, with only the two states of void and vacuum, corresponding to zero and , respectively, and since the change in the outward time is zero, and here we also consider , since the APPARENT VELOCITY does not change in this case, but we will also discuss relativistic mass in sectio ...
... e and Its Consequences on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics by Mohamed Haj Yousef [ PDF Download ] Search Inside this Book Method I (abrupt change of speed in the inner time): The RELATIVISTIC ENERGY -momentum relation is derived in section 6.2.8 further below, but the simple mass ...
... to zero and , respectively, and since the change in the outward time is zero, and here we also consider , since the apparent velocity does not change in this case, but we will also discuss RELATIVISTIC MASS in section 6.2.4 below; thus we obtain: ...
... e integration in equation 9 if, and only if , we suppose that the object, whose mass is , moves from rest to , or vice versa, in “zero time”, which of course will contradict the laws of PHYSICAL MOTION because the acceleration would be infinite, and hence the force and the energy. Ligh ...
... es on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics by Mohamed Haj Yousef [ PDF Download ] Search Inside this Book Method I (abrupt change of speed in the inner time): The relativistic energy- MOMENTUM RELATION is derived in section 6.2.8 further below, but the simple mass-energy equivalence ...
... course will contradict the laws of physical motion because the acceleration would be infinite, and hence the force and the energy. Light does in fact behave in this manner, for example: in PAIR PRODUCTION , or when emitted or absorbed; but the photon is massless, unlike other particles and ...
... [ PDF Download ] Search Inside this Book Method I (abrupt change of speed in the inner time): The relativistic energy-momentum relation is derived in section 6.2.8 further below, but the SIMPLE MASS -energy equivalence relation: (without the “half”) can now be easily obtained from ...
... rom zero to , which then becomes summation because it is an abrupt change, with only the two states of void and vacuum, corresponding to zero and , respectively, and since the change in the OUTWARD TIME is zero, and here we also consider , since the apparent velocity does not change in thi ...