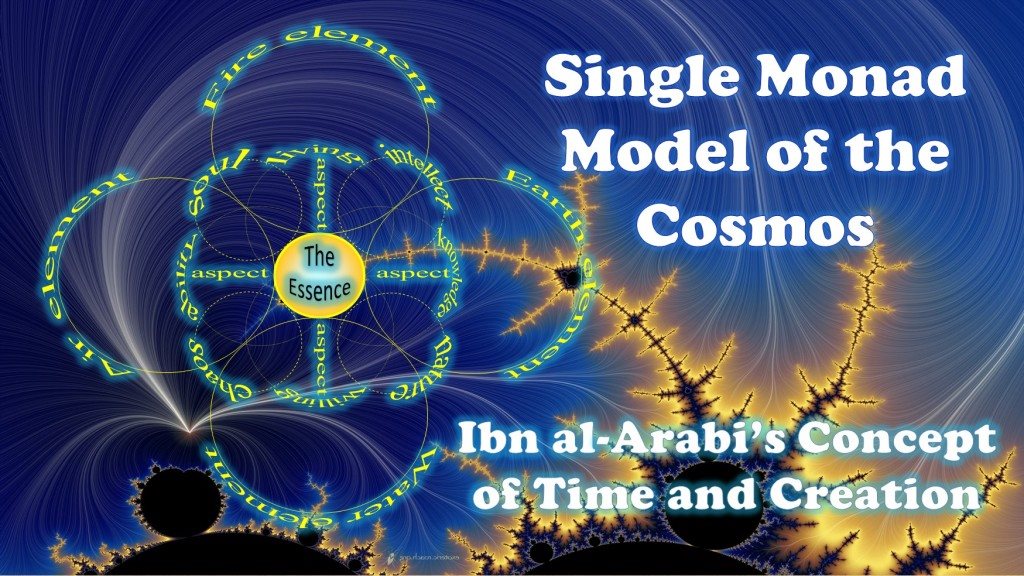
Most of these introductory articles are exracted from Volume I of the Single Monad Model of the Cosmos: Ibn al-Arabi's View of Time and Creation... more on this can be found here.
See also: Leibniz and Monadology
Time in Greek Philosophy
Since the age of Homer, the Greek word chronos was used to refer to time. Chronos was a Greek god who feared that his sons would take over his kingdom, so he ate them one after the other - just like time, which brings things into existence and then overtakes them.
We can already detect two clearly opposing views about time in the contrast between Plato's and Aristotle's schools of thought. Plato considers time to be created with the world, while Aristotle believes that the world was created in time, which is an infinite and continuous extension. Plato says: 'Be that as it may, Time came into being together with the Heaven, in order that, as they were brought into being together, so they may be dissolved together, if ever their dissolution should come to pass.' (Cornford 1997: 99)
Aristotle, however, believes that Plato's proposition requires a point in time that is the beginning of time and has no time before it. This notion is inconceivable for Aristotle, who adopts Democritus' notion of uncreated time and says: 'If time is eternal motion must also be eternal, because time is a number of motion. Everyone except Plato has asserted the eternity of time. Time cannot have a limit (beginning or end) for such a limit is a moment, and any moment is the beginning of a future time and the end of past time.' (Lettinck 1994: 562)
Thus time for Aristotle is a continuum, and it is always associated with motion; as such, it can not have a beginning (Lettinck 1994: 241-59, 361). Plato, on the other hand, considers time as the circular motion of the heavens (Cornford 2004: 103), while Aristotle said that it is not motion, but rather the measure of motion (Lettinck 1994: 351, 382, 390). Aristotle clearly relates rational time and motion, but the problem that arises here is that time is uniform, while some motions are fast and some slow. So we measure motion by time because it is uniform - otherwise it can't be used as a measure. To overcome this objection, Aristotle takes the motion of the heavenly spheres as a reference, and all other motions, as well as time, are measured according to this motion (Badawi 1965: 90). On the other hand, Aristotle considers time as imaginary because it is either past or future, and both don't exist, while the present is not part of time because it has no extension (Lettinck 1994: 348).
We shall see in Chapter II that Ibn al-Arabi shares with Aristotle the idea of a circular endless time and that it is a measure of motion, but he does not consider it as continuum. On the other hand, Ibn al-Arabi agrees with Plato that time is created with the world. In fact Plato was right when he considered time to be created, but Aristotle refused this because he could not conceive of a starting point to the world nor to time. Only after the theory of General Relativity in 1915, that introduced the idea of 'curved time', could we envisage a finite but curved time that has a beginning. By this we could combine Plato's and Aristotle's opposing views. However, Ibn al-Arabi did that seven centuries before, and he also explicitly spoke about curved time long time before Einstein.
... Space Transcendence Read this short concise exploration of the Duality of Time Postulate: DoT: The Duality of Time Postulate and Its Consequences on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics ...
... between Plato's and Aristotle's schools of thought. Plato considers time to be created with the world, while Aristotle believes that the world was created in time, which is an infinite and CONTINUOUS EXTENSION . Plato says: 'Be that as it may, Time came into being together with the Heaven, ...
... ut curved time long time before Einstein. Read Other Books: The Single Monad Model of the Cosmos: Ibn Arabi's View of Time and Creation The Duality of Time Theory: Complex-Time Geometry and Perpertual Creation of Space The Ultimate Symmetry: Fractal Complex-Time and Quantum Gravity The Che ...
... ndence Read this short concise exploration of the Duality of Time Postulate: DoT: The Duality of Time Postulate and Its Consequences on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics ...
... s ...
... ime for Aristotle is a continuum, and it is always associated with motion; as such, it can not have a beginning (Lettinck 1994: 241-59, 361). Plato, on the other hand, considers time as the CIRCULAR MOTION of the heavens (Cornford 2004: 103), while Aristotle said that it is not motion, but ...
... al-Arabi agrees with Plato that time is created with the world. In fact Plato was right when he considered time to be created, but Aristotle refused this because he could not conceive of a STARTING POINT to the world nor to time. Only after the theory of General Relativity in 1915, that i ...
... that has a beginning. By this we could combine Plato's and Aristotle's opposing views. However, Ibn al-Arabi did that seven centuries before, and he also explicitly spoke about curved time LONG TIME before Einstein. Read Other Books: The Single Monad Model of the Cosmos: Ibn Arabi's View ...
... t it is a measure of motion, but he does not consider it as continuum. On the other hand, Ibn al-Arabi agrees with Plato that time is created with the world. In fact Plato was right when he CONSIDERED TIME to be created, but Aristotle refused this because he could not conceive of a startin ...
... e motions are fast and some slow. So we measure motion by time because it is uniform - otherwise it can't be used as a measure. To overcome this objection, Aristotle takes the motion of the HEAVENLY SPHERE s as a reference, and all other motions, as well as time, are measured according to t ...
... s a number of motion. Everyone except Plato has asserted the eternity of time. Time cannot have a limit (beginning or end) for such a limit is a moment, and any moment is the beginning of a FUTURE TIME and the end of past time.' (Lettinck 1994: 562) Thus time for Aristotle is a continuum, ...
... ndence Read this short concise exploration of the Duality of Time Postulate: DoT: The Duality of Time Postulate and Its Consequences on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics ...