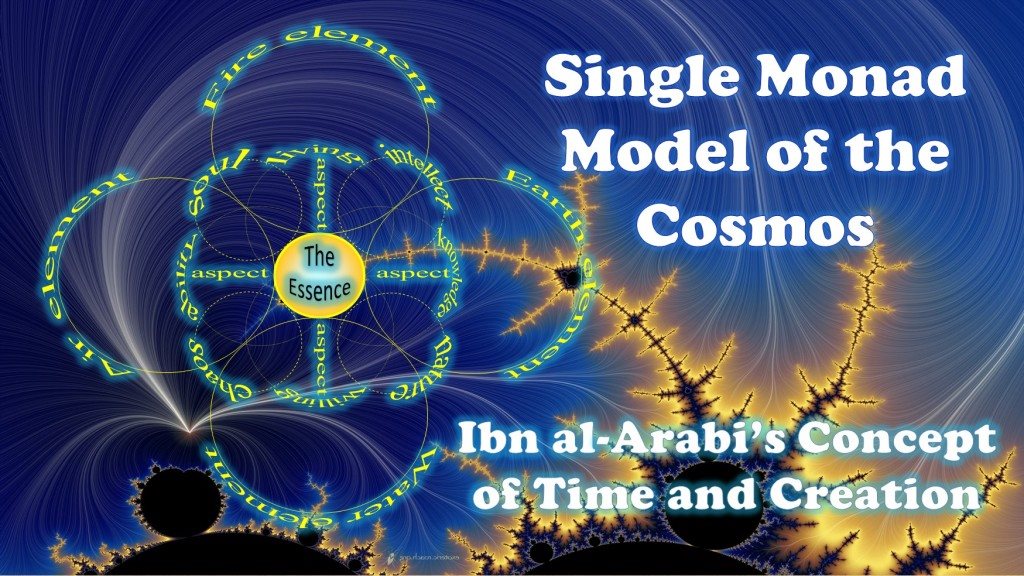
... Space Transcendence Read this short concise exploration of the Duality of Time Postulate: DoT: The Duality of Time Postulate and Its Consequences on General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics ...
... ng the mathematical basis of infinitesimal calculus. In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and gravitation, which allowed mathematical derivation of Kepler’s laws of PLANETARY MOTION , predicting the trajectories of comets, explaining tides and the precession of the ...
... er III. The principle remains central in modern physics and mathematics, being applied in thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, the theory of relativity, Quantum Mechanics, particle physics, and STRING THEORY . 2.16 Newton’s Mechanics Isaac Newton (1642-1726 AD) is considered one of ...
... we shall see in chapter III. The principle remains central in modern physics and mathematics, being applied in thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, the theory of relativity, Quantum Mechanics, PARTICLE PHYSICS , and string theory. 2.16 Newton’s Mechanics Isaac Newton (1642-1726 AD ...
... rajectories of comets, explaining tides and the precession of the equinoxes, in addition to other celestial and terrestrial motions. This theory removed all doubts about the validity of the HELIOCENTRIC MODEL . In return, this convinced most European scientists of the superiority of Newtoni ...
... ther celestial and terrestrial motions. This theory removed all doubts about the validity of the heliocentric model. In return, this convinced most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over the earlier corpuscular mechanical philosophy that we have reviewed in sect ...
... ics and mathematics, being applied in thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, the theory of relativity, Quantum Mechanics, particle physics, and string theory. 2.16 Newton’s Mechanics Isaac Newton (1642-1726 AD) is considered one of the most influential scientists in Western history. ...
... scientists in Western history. He laid the foundations of classical mechanics, in addition to his other contributions in optics. He is also credited, along with his contemporary philosopher Gottfried Leibniz (1646-1716 AD), for developing the mathematical basis of infinitesimal calculus. I ...
... dern kinetic energy. He realized that the total energy would be conserved in certain mechanical systems, so he considered it an innate motive characteristic of matter. Here too his thinking GAVE RISE to another regrettable nationalistic dispute. His vis viva was seen as rivaling the conser ...
... e equations of motion for that system. It can also be used to derive Newtonian, Lagrangian and Hamiltonian equations of motion, and even General Relativity, or what is known as the Einstein-Hilbert action. It has also been applied to derive important equations in Quantum Mechanics and Quan ...
... cs, in addition to his other contributions in optics. He is also credited, along with his contemporary philosopher Gottfried Leibniz (1646-1716 AD), for developing the mathematical basis of INFINITESIMAL CALCULUS . In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and gravitation, whic ...
... pher Gottfried Leibniz (1646-1716 AD), for developing the mathematical basis of infinitesimal calculus. In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and gravitation, which allowed MATHEMATICAL DERIVATION of Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, predicting the trajectories of ...